This article shows how to set up Fluentd with Graylog2. Graylog2 is a popular log analysis framework powered by Elasticsearch and MongoDB. Fluentd can output data to Graylog2 in the GELF format to take advantage of Graylog2's analytics and visualization features.
Prerequisites
- A basic understanding of Fluentd
- Ubuntu/Debian Linux
- sudo/root access
Setup
Dependencies
Install the dependencies with the following command.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install mongodb-server openjdk-7-jre-headless uuid-runtime adduser --yes
Elasticsearch
Latest Graylog2 requires Elasticsearch 1.7 or later, which can be installed with the following commands.
NOTE: Graylog2 doesn't support Elasticsearch 2.0 yet.
wget https://download.elasticsearch.org/elasticsearch/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-1.7.1.deb
dpkg -i elasticsearch-1.7.1.deb
Then, open
/etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml, find the line that sayscluster.name: elasticsearch
Uncomment and update it to
cluster.name: graylog2.
Also, for better security, disable dynamic scripting for Elasticsearch by adding the following line to
/etc/elasticsearch/elastcisearch.yml.script.disable_dynamic: true
Elasticsearch is ready. Start it with
sudo /etc/init.d/elasticsearch restart
Graylog2
In this article, we use Graylog2 1.2.
Get the GPG key.
wget -qO - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Graylog2/graylog2-puppet/master/files/RPM-GPG-KEY-graylog2 | apt-key add -
Update the package list.
echo 'deb http://packages.graylog2.org/repo/debian/ trusty 1.2' > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/graylog2.list
Finally, install Graylog's components.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install graylog-server graylog-web graylog2-stream-dashboard --yes
Edit
/etc/default/graylog-server and /etc/default/graylog-web and update RUN=no to RUN=yes.
Edit
/etc/graylog/server/server.conf and cocnfigure the following parameters:- password_secret
- root_password_sha2
For
root_password_sha2, run echo -n YOUR_PASSWORD | shasum -a 256 and copy and paste the output string. This "YOUR_PASSWORD" will be used later to log into Graylog2's web interface.
Edit
/etc/graylog/web/web.conf and configure the following parameters:- graylog2-server.uris="http://127.0.0.1:12900/"
- application.secret
Finally, start Graylog2!
sudo /etc/init.d/graylog-server restart
sudo /etc/init.d/graylog-web restart
Nginx (Optional)
If you are sharing access to Graylog2's web interface outside of your network, You need to set up a proxy server. Nginx is recommended.
First, install Nginx.
sudo apt-get install nginx --yes
Edit
/etc/nginx/sites-available/default so that it looks exactly like this:server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:9000/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_connect_timeout 150;
proxy_send_timeout 100;
proxy_read_timeout 100;
proxy_buffers 4 32k;
client_max_body_size 8m;
client_body_buffer_size 128k;
}
}
Then, restart nginx.
sudo /etc/init.d/nginx restart
Graylog2 GELF input
Go to . If Nginx was configured in the previous section, it should be served from port 80. Otherwise, it should be at port 9000.
To log in, use "admin" as the username and "YOUR_PASSWORD" from the Graylog2 server setup as your password.
Once logged in, click on "System" in the top nav. Next, click on "Inputs" from the left nav. (Or, you can just go to
<YOUR_ GRAYLOG2 URL>/system/inputs).
Then, from the dropdown, choose "GELF UDP" and click on "Launch new input", which should pop up a modal dialogue, Since the default values are good, fill the "Title" and just click "Launch".
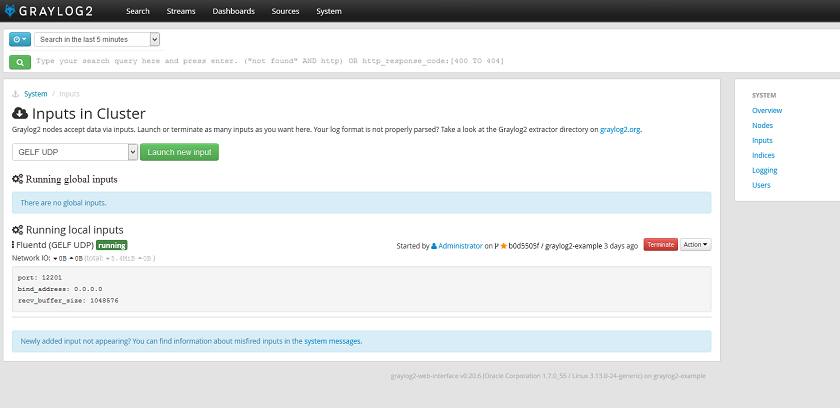
Now, Graylog2 is ready to accept messages from Fluentd over UDP. It's time to configure Fluentd.
Fluentd
See here for all the download options. Here, we are using the Trusty deb package.
curl -L http://toolbelt.treasuredata.com/sh/install-ubuntu-trusty-td-agent2.sh | sh
Then, install the
out_gelf plugin to send data to Graylog2. Currently, the GELF plugin is not published to Rubygems, so we download the plugin file and place it in /etc/td-agent/plugin. We also need to gem-install GELF's Ruby client./usr/sbin/td-agent-gem install gelf
cd /etc/td-agent/plugin
sudo wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/emsearcy/fluent-plugin-gelf/master/lib/fluent/plugin/out_gelf.rb
Finally, edit
/etc/td-agent/td-agent.conf as follows.<source>
type syslog
tag graylog2
</source>
<source>
type tail
format nginx
path /var/log/nginx/access.log
tag graylog2.nginx
</source>
<match graylog2.**>
type copy
<store>
type gelf
host 0.0.0.0
port 12201
flush_interval 5s
</store>
<store>
type stdout
</store>
</match>
That configuration listens to two data sources:
- Nginx access log of Graylog2 web app itself. Admittedly, this is a toy example, but it showcases the in_tail plugin.
- It listens to syslog input. Fluentd automatically parses common fields such as
ident.
We need to make a couple of tweaks to successfully ingest Nginx access logs and syslogs.
- Run
sudo chown -R td-agent:td-agent /var/log/nginxso that Fluentd can read Nginx access logs. - Open
/etc/rsyslog.confand add the following line to the beginning of the file:*.* @127.0.0.1:5140Then, restart rsyslogd by runningsudo /etc/init.d/rsyslog restart.
Finally, start Fluentd with the following command.
sudo /etc/init.d/td-agent restart
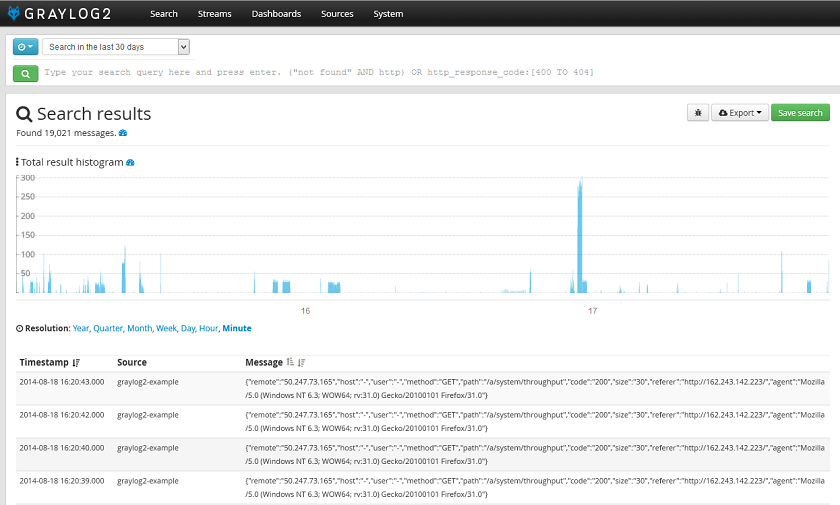
Confirming the setup inside Graylog2's UI
When you log back into Graylog2, you should be seeing a graph like this (wait for events to flow in)
What's Next?
Interested in other data sources and output destinations? Check out the following resources:
Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire